Diabetes, a complex condition affecting millions of people worldwide, continues to challenge modern healthcare systems. Understanding the intricacies of this chronic disease and learning to manage it effectively is vital for maintaining good health and preventing debilitating complications.
In this blog post, we’ll unravel the mystery of “what is diabetes” and provide essential insight into its types, symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies.
Key Takeaways
-
- Understanding diabetes is essential for managing the disease and minimizing related health risks
- Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly, can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- Taking measures to regulate blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can reduce potential complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetes

Diabetes is a long-term health issue associated with high blood sugar levels that, if not managed, can cause several health problems, including high blood pressure. Damage to blood vessels in the heart, eyes, kidneys, and nerves is a known consequence of diabetes, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and even permanent vision loss.
Furthermore, nerve damage and poor blood flow in the feet often lead to foot ulcers and, in severe cases, amputations.
The fundamental aspect of diabetes involves the interaction of blood sugar, insulin, and glucose regulation. Grasping these relationships and their impact on the body is key to managing diabetes and lowering the risk of severe health complications.
Video: Know Diabetes by Heart
Blood Sugar and Insulin
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a pivotal role in the body’s ability to use glucose from carbohydrates in food for energy or to store glucose for future use. Diabetes occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly.
Glucose, commonly called blood sugar, is a key source of energy for cells in muscles and other tissues. It helps them carry out their daily activities. Insulin aids the entry of glucose into cells for energy use, thereby maintaining appropriate glucose levels in the body.
In a healthy individual, insulin signals the liver, muscle, and fat cells to take in glucose from the blood, lowering blood glucose levels and keeping them within a normal range. When insulin works effectively, the blood sugar level drops.
However, when there is a deficiency or absence of insulin in the body, glucose is unable to enter the cells to be utilized as energy, causing elevated blood sugar levels and potential health complications.
Losing weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The Importance of Glucose Regulation
Glucose is of paramount importance to the human body as it is the primary source of energy for the cells. It furnishes fuel for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration and is indispensable for neurotransmission and cellular survival. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to complications such as digestive and kidney diseases.
Elevated glucose levels may result in symptoms such as extreme thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and increased hunger. Over time, high blood sugar levels can also cause harm to the body’s organs and lead to poor blood flow. Low glucose levels, or hypoglycemia, may provoke symptoms such as shaking, rapid heartbeat, sweating, anxiety, dizziness, extreme hunger, weakness, and tiredness. Hence, maintaining glucose levels is fundamental for the overall health and well-being of individuals with diabetes.
Types of Diabetes: A Closer Look

There are several types of diabetes, each with unique characteristics that require tailored management approaches. The most prevalent forms of diabetes include type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of the disease, with 90-95% of all diabetes cases attributed to it. It’s far and away the most prevalent type. However, other types of diabetes also exist, such as prediabetes, a condition characterized by blood sugar levels that are higher than average but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Comprehending the distinct types of diabetes, their specific causes and their traits are essential for effective management and prevention. The subsequent sections will detail type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes, and their impact on those affected.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body produces limited or no insulin due to the immune system attacking and eliminating the cells responsible for insulin production within the pancreas. This type of diabetes is typically diagnosed in children and young adults, though it may manifest at any age.
Individuals with type 1 diabetes require daily insulin injections to survive, as their bodies cannot produce the necessary insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. It is estimated that 9 million people had type 1 diabetes in 2017.
Though type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, those diagnosed need to meticulously manage their blood sugar levels using insulin therapy and other medical interventions. Early diagnosis and proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a condition wherein the cells of the body are not utilizing insulin effectively, and the pancreas is not producing enough insulin to maintain blood glucose levels within the normal range. This type of diabetes is caused by a combination of factors, such as:
-
- overweight or obesity
- physical inactivity
- insulin resistance
- genetic or family history
Treatment for type 2 diabetes typically consists of tablets or injections, and in some cases, the condition can be put into remission by achieving weight loss.
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes has been steadily increasing in recent years, making it all the more important for individuals to be aware of the risk factors and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Preventative measures, such as maintaining a healthy weight, implementing sustainable dietary and physical activity modifications, and undergoing regular blood sugar monitoring, can be effective in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition that occurs during pregnancy, often caused by factors such as being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, and experiencing hormonal changes during pregnancy. While some women with gestational diabetes may experience increased thirst, more frequent urination, and fatigue, others may exhibit no discernible symptoms. Gestational diabetes has the potential to cause complications in both the mother and the baby, making proper management and monitoring during pregnancy crucial.
After giving birth, most women with gestational diabetes see their blood sugar levels return to normal. However, they are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life, making it essential for them to maintain a healthy lifestyle and undergo regular blood sugar checks to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is essential for early diagnosis and intervention, as timely treatment can help prevent or manage potential complications. The primary indications of diabetes include weight loss, increased thirst, and frequent urination. However, these symptoms can vary depending on the type of diabetes. For example, type 1 diabetes symptoms typically present rapidly and are more severe than those associated with type 2 diabetes.
In some cases, such as gestational diabetes, there may be no discernible symptoms, highlighting the importance of regular prenatal checkups.
Being vigilant about potential signs and symptoms of diabetes is crucial for both individuals at risk and those already diagnosed with the condition. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals can help ensure timely diagnosis and management, improving the chances of living a healthy life with diabetes.
Risk Factors and Prevention
Diabetes can be attributed to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While some risk factors, such as family history and ethnicity, cannot be modified, lifestyle choices play a significant role in the development and management of diabetes. Understanding these risk factors and making appropriate lifestyle changes can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
The subsequent sections will examine the genetic and environmental influences on diabetes, as well as the role of lifestyle choices in prevention. This information will equip you with the knowledge to make decisions about your health and well-being.
Genetic and Environmental Influences
Family history, ethnicity, and other genetic factors can influence the development of diabetes. For instance, people from the following backgrounds are at a heightened risk of developing type 2 diabetes:
-
- Black African
- African Caribbean
- South Asian
- Hispanic/Latino
However, no particular ethnicity is associated with an increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes.
Environmental factors that can contribute to the risk of developing diabetes include:
-
- Air pollution
- Poor dietary habits
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Stress
- Exposure to environmental hazards
Being aware of these genetic and environmental risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to minimize their risk of developing diabetes.
Lifestyle Choices
Leading a healthy lifestyle is a key factor in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, low-fat dairy, and healthy fats, can help maintain proper blood sugar levels and overall health.
Regular exercise has been shown to lower blood glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, enhance glucose disposal, manage weight, and reduce cardiovascular risk factors, thus providing a beneficial impact on diabetes management.
Prioritizing healthy lifestyle choices, like balanced eating and regular exercise, can markedly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, those already diagnosed with diabetes can improve their blood sugar control and minimize the risk of complications by adopting and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
For most people with diabetes, The American Diabetes Association recommends fasting or before meals blood glucose {or blood sugar) goal of 70-130 mg/dl. One to two hours after eating, postprandial blood sugar reading at or under 180 mg/dl is recommended
Managing Diabetes: Treatment Options and Self-Care
Effectively managing diabetes is vital to prevent complications and maintain overall health. Treatment options for diabetes vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Medications, insulin therapy, and self-care strategies, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, play a crucial role in managing diabetes.
The upcoming sections will discuss various treatment options and self-care strategies for individuals with diabetes, enabling them to manage their condition and lead healthy lives.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
A variety of medications are utilized to treat diabetes, including insulin, sulfonylureas, biguanides, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, dopamine-2 agonists, incretin mimetics, bile acid sequestrants, and other contemporary medications.
Insulin therapy, in particular, is highly efficacious in regulating blood sugar levels and averting diabetes complications. Different types of insulin include fast-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulin, as well as insulin aspart, insulin glulisine, and insulin lispro.
Working closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medications and dosages is essential for effective diabetes management. In addition to medications, individuals with diabetes should also engage in healthy living strategies, such as:
-
- Following a balanced diet
- Regular physical activity
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Managing stress
- Getting enough sleep
These strategies, combined with medication, can help individuals with diabetes effectively manage their condition.
Healthy Living Strategies
A balanced diet, regular exercise, and other healthy habits are integral to managing diabetes and reducing complications. Nutritious eating helps maintain blood sugar levels, while regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity and minimizes cardiovascular risk factors. Two diets recommended for diabetes are the Mediterranean diet and a diet that includes foods with a low glycemic index.
Implementing healthy living strategies can help individuals with diabetes improve their blood sugar control, minimize the risk of complications, and boost their overall quality of life. It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that incorporates these strategies.
Potential Complications and Their Prevention

Diabetes can cause a variety of complications like nerve damage, digestive issues, and erectile dysfunction. Regulating blood glucose, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels can help alleviate these risks. For example, regulating blood glucose levels can help prevent damage to the eyes.
The subsequent sections will discuss potential complications of diabetes, including heart and blood vessel damage, and nerve and kidney damage, and outline steps that can mitigate these risks.
Heart and Blood Vessel Damage
Diabetes can contribute to blood vessel damage through a process known as atherosclerosis, which is characterized by the accumulation of plaque in the arteries. Over time, elevated blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels, resulting in reduced blood flow and an increased risk of vascular complications, including heart disease. People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to develop cardiovascular disease than those without.
Proper management of diabetes through lifestyle changes and medical interventions is key to preventing complications like heart and blood vessel damage. Here are some strategies to help reduce the risk of these complications:
-
- Monitoring blood sugar levels
- Consuming a nutritious diet
- Exercising regularly
- Taking medications as prescribed
By following these strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Nerve and Kidney Damage
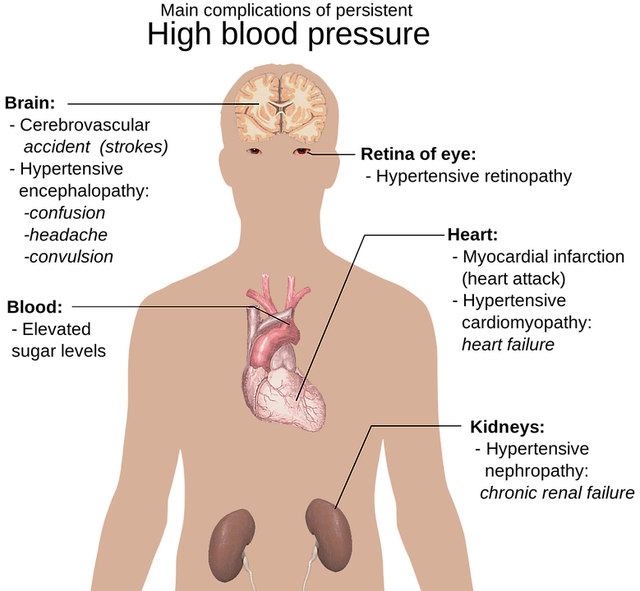
Diabetic nerve and kidney damage can potentially result in ulcers, infections, and in some cases, amputations. It can also lead to renal failure. Diabetic foot problems can result in nerve damage and reduced blood supply to the feet, which can ultimately lead to ulcers, infections, and in some cases, amputations. Diabetic nephropathy is a long-term kidney disease caused by diabetes and is the leading cause of kidney failure in adults.
To reduce the risks of diabetic nerve and kidney damage, it is advised that adults with diabetes should have their feet examined annually by a healthcare professional. It is imperative to seek medical assistance promptly if any irregularities are detected in the feet.
Summary
Unraveling the mystery of diabetes is key to managing this complex condition effectively. By understanding the types of diabetes, recognizing symptoms, identifying risk factors, and implementing treatment options and self-care strategies, individuals with diabetes can take control of their condition and maintain a healthy, fulfilling life. Remember, early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the first signs of being diabetic?
Common early signs of diabetes include frequent urination, increased thirst and fatigue, and sudden weight loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, see a doctor about getting tested for diabetes.
How do people cope with diabetes?
Managing diabetes effectively requires healthy eating, exercise, and emotional support. Coping with the stress of diabetes is important to managing blood glucose levels; this can be achieved through activities such as exercise, meditation, and seeking a mental health professional.
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system attacks the pancreas, preventing it from producing insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the pancreas produces less insulin than needed, and the body is resistant to the insulin that is present.
Can lifestyle choices help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes?
Yes, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, implementing dietary and physical activity modifications, and regular blood sugar monitoring can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
What are the potential complications of diabetes?
Diabetes can have serious consequences, such as nerve damage, digestive problems, and erectile dysfunction.
Why is weight loss so important?
Weight loss increases insulin sensitivity which allows cells to move effectively to use the insulin in the body. Losing 10 to 20 pounds can accomplish a number of benefits, such as improved blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol.
Will insulin make me gain weight?
Insulin’s job is to process calories and it doesn’t cause weight gain. You must practice portion control.

